What States Are In The Rust Belt?

The Rust Belt includes the following states:
- New York
- Pennsylvania
- West Virginia
- Ohio
- Michigan
- Wisconsin
- Indiana,
- llinois
- Missouri
But there is so much more to learn about the Rust Belt than what states make it up!
The Rust Belt in the United States has a fascinating name and an intriguing history. Although this is a colloquial term that refers to a geographic region, it tells us a lot about the people who used to live in this area and what they used to do.
In this post, we’ll talk about the states that make up the Rust Belt. We’ll also share some interesting historical facts about how it got its name and what it looks like now.
Contents
Advertising Disclosure: What States is a for profit reference website, supported by advertisements. Thank you for supporting our mission to make geography fun for all!
What States Are the Rust Belt?
The Rust Belt includes New York in the North East, Pennsylvania, West Virginia, Ohio, Michigan, Wisconsin, Indiana, Illinois, and Missouri in the Midwest.
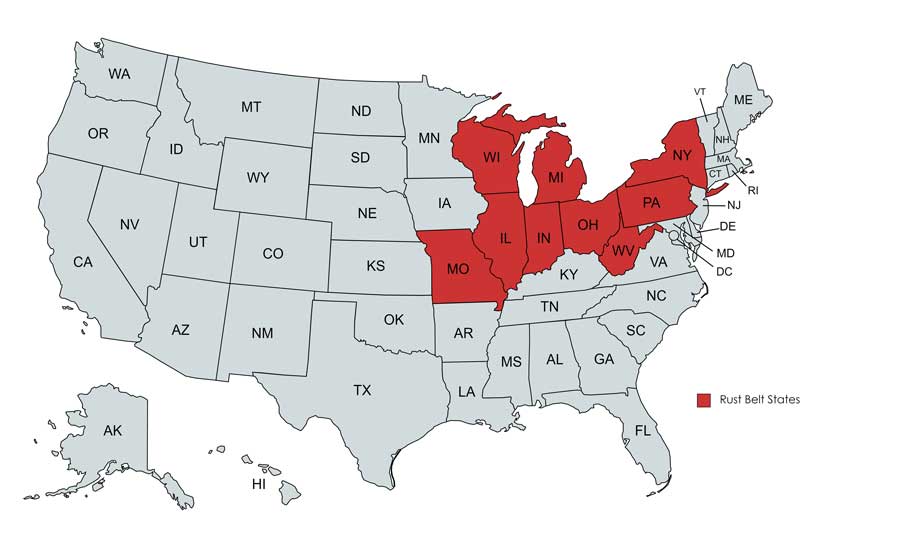
Where is the Rust Belt Located?
The Rust Belt is a belt region of the US that refers to a geographical region that stretches from the Midwest to the Northern states (ending just before the states that make up New England). In the past, this region became an industrial hub because it was close to the Great Lakes and rivers that companies and factories used to access raw materials.
What Does the Rust Belt Refer To?
The Rust Belt refers to the cities and states in the Midwest that were once home to some of the greatest factories in the USA. It was home to millions of blue-collar workers and their families who managed to make the area boom at the beginning of the 20th century.
Why Is it Called the Rust Belt?
In the past, this region was called the Steel Belt, Factory Belt, or Manufacturing Belt, as this area was known for steel manufacturing and heavy industries that boomed at the beginning of the 20th century.
However, in the middle of the 20th century, and especially after World War II, the economy in this area greatly suffered, and gaining access to raw materials became challenging. At the same time, relying on manufacturers from outside the USA affected these industries greatly.
As a result, cities of the Rust Belt experienced a significant decrease in population, especially in the 50s and 60s, and the steel equipment turned to rust because nobody was using it. In the late 70s, these cities and states received the name Rust Belt to signify the loss of population and the increase in idle equipment and factories that were left to rust.
⛪ Trivia Time: What states are part of the Bible Belt? Learn the surprisingly controversial answer!
How the Rust Belt Has Changed Over the Years

The significant decline in income that families in the Rust Belt had to deal with forced many of them to leave and move to other parts of the country. The area was deindustrialized as factory owners were going out of business and shutting down their factories. With no other income source, the area was left with high poverty rates and very few high-earning jobs, which led to public discontent.
Workers were being replaced with more advanced technology that led to the loss of jobs. At the same time, factory owners were unable to offer their products at competitive prices because of the increase in raw materials prices.
After World War II, the American economy was subject to heavy competition coming from Asia and Europe, offering low-priced products that were more appealing to consumers. Some manufacturers also lost their capital due to the stress the war imposed on every part of the economy. All these reasons affected the heavy industries that once made the Manufacturing Belt the industrial heart of the USA.
❓ Trivia Time: What States Are Part of the East Coast? (We bet you can’t guess them all!)
This led to a change in the urban landscape as the local population moved to other states to seek better jobs. Some blue-collar workers moved overseas for the money, while others tried to find other jobs. Some factories tried to cope with the new challenges and trained their workers to use the latest technology, but a smaller workforce was still needed to deliver the same products.
As a result, these states began to experience the highest poverty rates in the 60s. Today, these states still have higher poverty rates compared to other states in the USA.
These states are still experiencing a big decline in population. For example, some cities like Decatur, Illinois, Flint, Michigan, Buffalo, New York, and Cleveland, Ohio have experienced a population decline of more than 25% in the recent years between 2000 and 2016.
Fun Facts About the Rust Belt
- The Rust Belt was known for several industries, including coal plants, steel plants, automotive and aviation production, and weapons production.
- In the 1930s and early 1940s, the Rust Belt represented the American Dream, with booming industries and high-paying jobs that attracted skillful workers from every part of the USA. It was referred to as the American Economic Miracle due to the increase in income that made the region lucrative for blue-collar workers and their families.
- The term Rust Belt was forgotten for a few years until Trump used it in his elections. As Trump focused on imposing several constraints on foreign trade, he drew attention to the problem of the Rust Belt and how his policies are trying to prevent this from reoccurring. As a result, politicians attribute Donald Trump’s success in the 2016 elections largely to the support he received from the Rust Belt cities.
- At its peak, the Rust Belt was home to almost 1.8 million people. This number reached about 673,000 people in 2018.
FAQs About the Rust Belt
Did Any Other Country Experience Rust Belts?
Yes, countries like China, Germany, and Russia faced a similar issue after the war. These regions refer to areas in the country that was once full of several successful heavy industries but aren’t now.
What is Happening in the Rust Belt Now?
As of 1980, the Rust Belt cities have been trying to build themselves back. People are going back to the factories by replacing the old equipment with new and advanced ones. Workers are being trained to work with and understand the new technology to deliver high-quality products.
This transition has been accompanied by downsizing, although the government was offering low-energy prices to help improve the levels of unemployment.
Today some cities in the Rust Belt, including Detroit and Cleveland, are trying to diversify their economy by transitioning to the service information economy. Still, education reforms are needed to create better jobs for the region’s residents.
❓ Trivia Time: What States Are The Midwest?